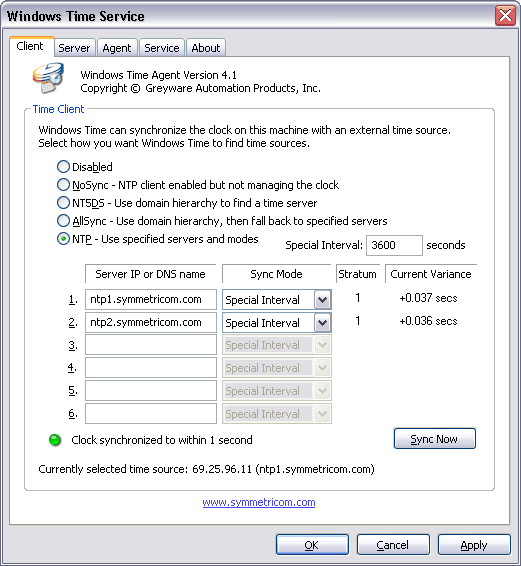
 Domain Time II Windows Time Agent: Client tab The Windows Time service can be set to a variety of methods to obtain the time and set the local clock. Use the radio buttons to select the method you prefer. Consult the Microsoft Windows Time documentation for a description of each of these options.
The client portion of Windows Time service will not be loaded.
NoSync
NT5DS
AllSync
NTP
If Special Interval is selected as the NTP sync mode (see below), this field allows you to specify the number of seconds to wait between attempts to synchronize the system clock. This setting corresponds to the SpecialPollInterval value in the [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\TimeProviders\NtpClient] registry key. Use the time source fields to enter the IP address or DNS name of NTP time sources you want the Windows Time service to synchronize with.
The Sync Mode dropdown box allows you to select the NTP sync mode to use: Visual status indicators and Sync Now The Sync Now button will instruct the Windows Time service to resynchronize with its time source. The sync may not occur immediately, it happens according to the internal schedule of the time service. The applet will constanly display the current clock variance of each selected source, as well as an idicator light showing the sync status of the local clock. The currently selected time source (inbound time partner) is displayed as well.
Co-existing with the Windows Time Service
|