Version 4.1 The Domain Time II Management tools include many useful diagnostic and utility programs. These utilities are installed automatically when Manager is installed, and are located in the Domain Time II Program Folder (usually C:\Program Files\Domain Time II).
Use the Remote CPL utility to quickly connect to a Domain Time II Server or Full Client and change its Control Panel Applet settings. This is a useful utility when all you need to do is change a control panel applet setting and you don't need the full power of Domain Time II Manager.
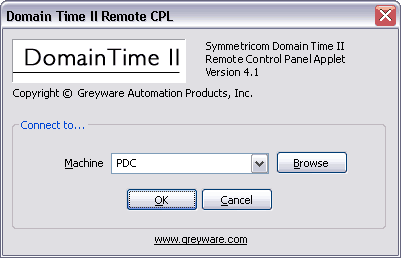 The Domain Time II Remote CPL Utility
The DTRCPL utility is subject to the same requirements as Domain Time II Manager in order to connect to and control a remote system:
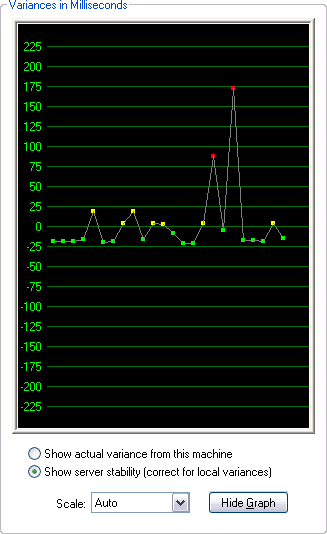
DTTest Use this utility to test the clock stability of any time server. Use it to determine which servers to use as time sources, or to troubleshoot accuracy issues.
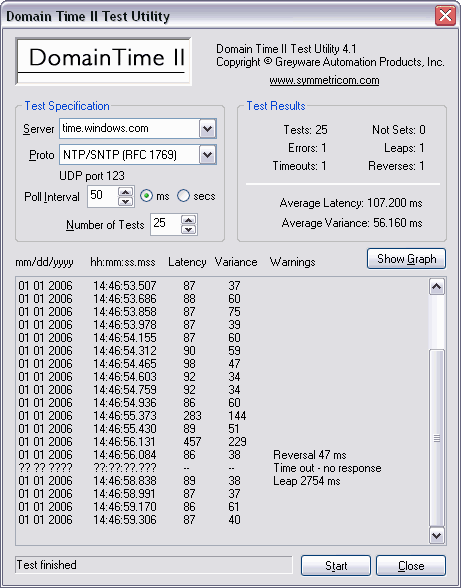 The DTTest Time Test Utility
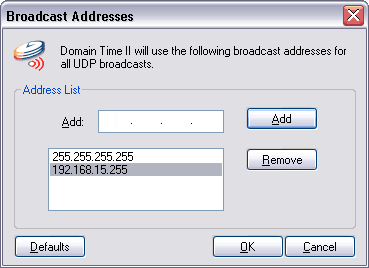
DTProbe This utility details the Domain Time II automatic server discovery process and shows which time servers a client running automatic settings will find and use. Use this utility any time you're troubleshooting time synchronization issues.
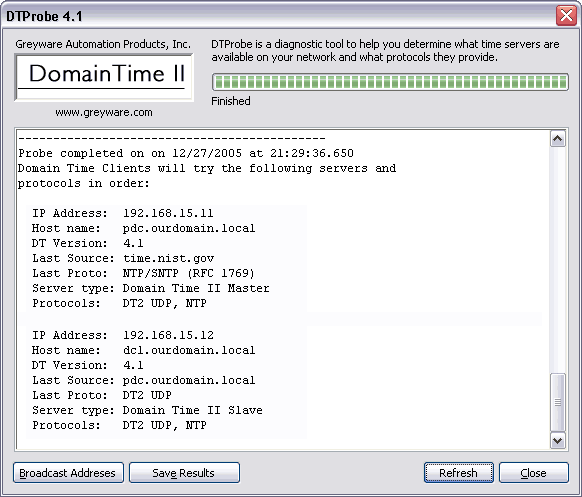
This utility performs the same server discovery process that the Thin Client, Full Client (in automatic mode), and the domtimed daemon (automatic mode) perform when they attempt to discover a time server. This process is detailed and recorded by the utility so that you can see exactly what servers are available to clients.
Use the Broadcast Addresses button to modify the broadcast addresses used by the utility. To be useful, these entries should duplicate the ones that the client uses (usually 255.255.255.255) - see the discussion about setting the client broadcast addresses using Manager via the Options button on the Connection Details screen. See also the Working Across Subnets page for more information. Click the Start button to perform the scan. Click the Save Results button to pull the results up in Notepad so that you may save them wherever you want.
Use LMCheck to obtain a quick variance report and save the results to a file. Use this tool to do a quick & dirty check of network synchronization on a network that doesn't already have Domain Time II installed.
NOTE: This product has been deprecated
Time variances from the machine on which you run LMCheck are calculated and displayed, taking into account any network latencies. You may select the domain you wish to scan from the drop-down list.
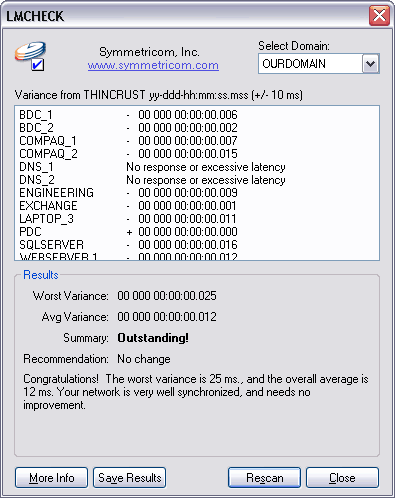 A fully synchronized network The LMCheck tool runs on either 32-bit systems or 64-bit Windows systems, although it can scan any machine running Microsoft Networking that responds to NetRemoteTOD queries.
Click the Start button to perform the scan. Click the Save Results button to pull the results up in Notepad so that you may save them wherever you wish. Note that the variance report generated by LMCheck cannot be as detailed or as accurate as variance reports provided by the Domain Time II Manager, the Monitor Service, the DTCheck utility, or Domain Time II Audit Server, each of which use much more accurate time protocols and sampling methods to measure the time differentials. Also, LMCheck cannot measure any systems not running Microsoft Networking. Generally, you will want to use LMCheck to obtain a quick snapshot of the time variance on networks where Domain Time is not yet installed. Although it is included as part of the licensed Domain Time II Management Tools, LMCheck itself is unsupported freeware, and can be freely distributed as long as the program is unmodified.
DTCheck This multi-purpose utility can check statistics, trigger Domain Time synchronizations, check clock accuracy, and generate high-accuracy variance reports, and more. This is a very handy tool to use if you're at a workstation that doesn't have Domain Time II Manager installed.
 DTCheck Parameters and Options Display You can examine the statistics (sample) of any Domain Time II server or client, force the synchronization of a particular machine (or of the entire time hierarchy), and generate a system-wide variance report (sample). Note: DTCheck's variance reporting is much more accurate than LMCheck utility, since it uses higher accuracy protocols and sampling methods from installed Domain Time II components. Use this utility for variance reports on networks that have Domain Time Servers and Clients installed. DTCheck can also be used to test your machine's clock for reliability. Run DTCheck /test to test your machine. You will probably need to reset the time after testing, since DTCheck will change the clock during the test. DTSync Use this utility to trigger a sync on specified machines from the command line.
 DTSync Parameters and Options Display DTSync allows you to specify timeouts and to set the ERRORLEVEL variable so you can create robust batch files to reliably trigger synchronization, even across WAN links. NTPCheck A utility for testing NTP/SNTP time servers. Use this utility if you need to save NTP server tests to a file, or want to run regular tests in a batch file.
NTPCheck is also useful for demonstrating the limits of NTP/SNTP accuracy. With the -raw option, you can see the results of other information derived from the NTP packets. For example, here are two actual sample reports generated by querying time.nist.gov. The first query shows the standard NTPCheck response; the second query shows the results of the -raw option.
 NTPCheck Parameters and Options Display 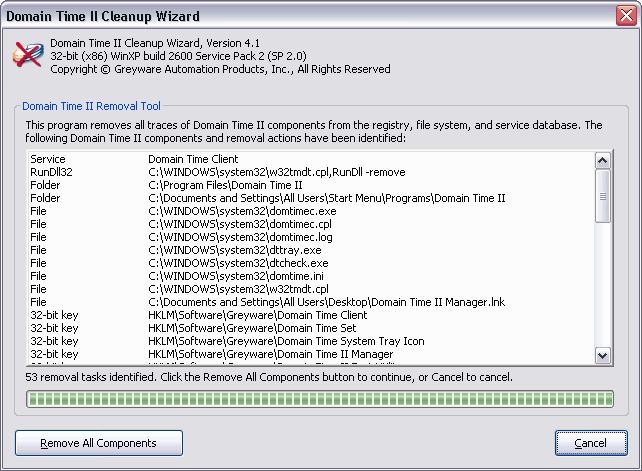 The Domain Time II Removal Tool (DTCLean)
DTClean keeps a log of the components it removes, and you may save a copy of the log file for troubleshooting purposes or to supply to technical support if requested.
|