Note: Settings on this page do not change the roles of other machines; they only affect how this master treats them. Two different classes of Domain Time II slaves are displayed here - slaves that are part of the same Windows domain as the master server (known as Domain Slaves), and slaves that are not part of the master's domain (known as Foreign Slaves).
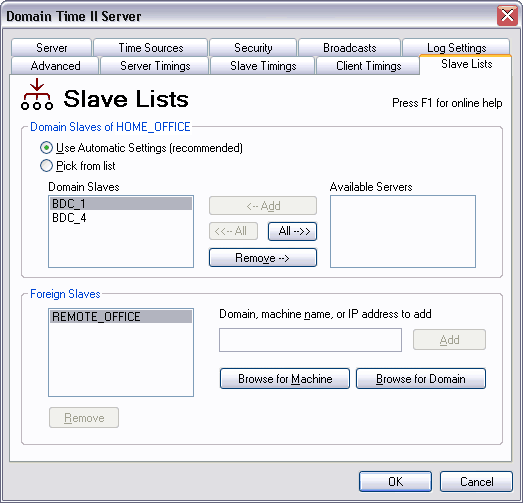 The Domain Time II Control Panel Applet - Slave Lists Tab This section shows you which machines this master server currently knows to be slaves in your domain.
Domain Slaves (by default, all DCs running Domain Time II Server) receive and act upon these control messages sent from the master server:
See Cascading Time Hierarchy for more information on these items.
Use Automatic Settings (Recommended) When this box is checked, the master server will automatically identify slaves in its domain. We recommended that you allow the master to run with the Use Automatic Settings box checked; this assures that the master/slave relationships operate correctly, and that the master will identify new slaves as they appear.
Allows you to edit the list of Domain Slaves.
Although Use Automatic Settings is the correct choice for most situations, there may occasionally be times when you will want to adjust the server's list of domain slaves manually. For example, if you have a slave machine that no longer exists or is offline for a long period of time, the master server logs will include connection error messages each time the master sends a Level-1 cascade signal to the slaves. Moving that server to the Available Servers list will stop the warning messages. Note that moving an independent server from the list of Available Servers into the Domain Slaves list will not turn an independent server into a slave. Independent servers always ignore Level-1 cascade signals; this configuration will not produce warning messages on either the independent server or its master. When the Pick from List box is checked, any new slave servers created will not be added to the Domain Slaves list automatically; they will show up in the Available Servers column instead and won't receive Level-1 cascade signals until you manually move them to the other column. This section shows you the domains (or machines) that have registered as foreign slaves of this master. Foreign Slaves receive and act upon Level-1 cascade signals, but otherwise behave according to their server role. This allows you to combine multiple domains into a single time hierarchy, letting one master synchronize all the others. The Foreign Slaves section of the Slave Settings tab on the overall master shows those domains that have registered themselves with the master as being foreign slaves.
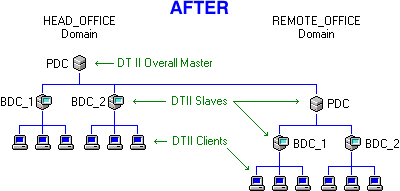
Important Concepts: Any master or independent server in another domain can become a foreign slave of this domain if you check its Set this machine to be a slave of a foreign master checkbox (see Time Sources). That machine will then register itself as a foreign slave of this domain, and begin to receive Level-1 cascade signals as if it were a normal Domain Slave. For example, say your company has two domains: HEAD_OFFICE and REMOTE_OFFICE. Installing Domain Time II on the PDC of each domain results in two master Servers, operating independently of each other. This can be inconvenient, particularly if you need to open firewall access for each server and configure each server individually.
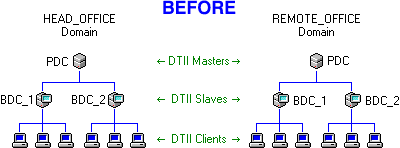 By setting the REMOTE_OFFICE domain to be a foreign slave of HEAD_OFFICE, you avoid these problems. The REMOTE_OFFICE master will now automatically get its time from the HEAD_OFFICE master just as if it were a slave in the HEAD_OFFICE domain. The REMOTE_OFFICE master will continue to act as the master server in its own REMOTE_OFFICE domain, serving time exactly as before to its own slaves and clients (or even its own foreign slaves).
Adding and Removing Foreign Slaves
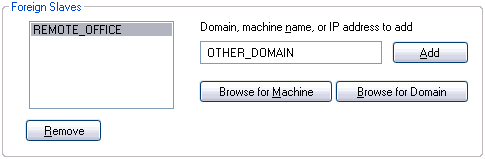 The Domain Time II Control Panel Applet - Adding/Removing Foreign Slaves Also, you may find that your particular domain browsing or network configuration prevents foreign slaves from registering themselves with the overall master correctly. In that event, you can add the slave manually by specifying the foreign domain name, DNS Name, IP address, or even the NETBIOS name. Note that adding a Foreign Slave to the list manually will not turn a remote machine into a slave. You must also check the Set this machine to be a slave of a foreign master checkbox on the other machine.

|